A sourdough starter, levain, chef, lievito madre, mother dough, mum, and so many more names—it can get a bit confusing. What is what, and when is it used? This post focuses on two foundational blocks in baking sourdough bread: a sourdough starter and a levain. And while there are many names for these two and other preferments, let’s dig in and look at what is a levain and how is it different from a starter.
The world of preferments is vast, each with different flour and water ratios and names. A preferment is essentially a mixture of flour, water, and a leavening agent (in our case, a sourdough starter) left to ferment before mixing everything into a final dough. Preferments help bring flavor, aroma, and keeping qualities to your bread. The extra fermentation time contributes additional byproducts of fermentation to your dough in the form of organic acids and alcohols—flavor. You can also use a preferment to skew the populations of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and wild yeast, which has an effect on taste and texture in the final dough as it in turn ferments.
At their core, though, both a starter and a levain fall under the same category as a preferment. They are mixed ahead of time, left to ferment, and then either used directly in the dough (levain and sometimes starter) or refreshed to keep the culture alive (starter).
And if you’re wondering, yes, the prefermented flour percentage you’ll often see in recipes is the percentage of flour that’s fermented ahead of time with respect to the total flour in a recipe. This percentage gives you an idea of how considerable the preferment is relative to the rest of the recipe’s flour. Ultimately, this has implications for flavor, the recipe timetable, and more.
Let’s start at the beginning.
What is a Sourdough Starter?
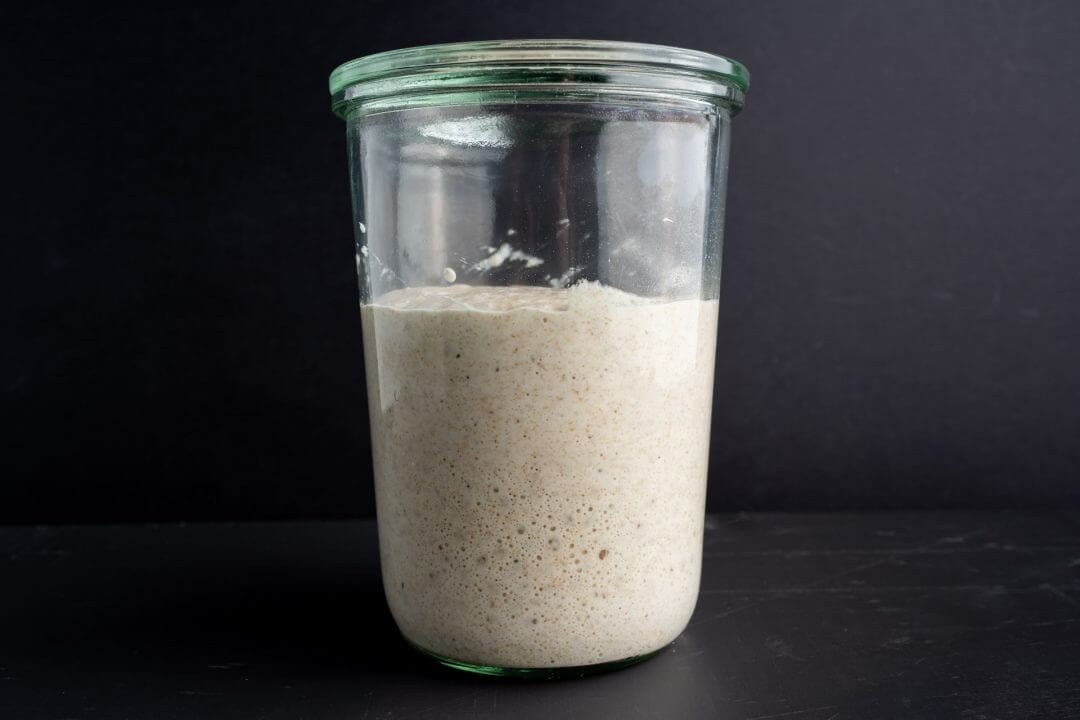
A sourdough starter is a combination of wild yeasts and suitable bacteria that can live indefinitely if properly maintained. This starter can be used to seed fermentation in new bread dough, used to make a levain, or refreshed (discarded and new flour and water added) to continue it’s life.
You will never use your starter up entirely in a single bake. You might take part of your starter to mix directly into a dough, but you will always keep some to keep the culture going. And if you don’t use some starter to mix directly into a dough, you can create a small off-shoot to scale up the preferment, change its flour makeup, or hydration. This off-shoot is called a levain.
An exception to this is the pâte fermentée, or “old bread” method. In this approach, no starter is maintained separately; a small piece of dough is taken from a batch of dough and kept until the next day to continue the culture. While bakers have used this method throughout history, I prefer to keep a separate jar with my starter inside. This approach helps avoid the unfortunate circumstance of forgetting to save a bit of dough and creating a new starter from scratch.
Check out my 21 most common starter problems (with solutions) →

What is a Levain?
A levain, also called a leaven or levain starter, is an off-shoot of your sourdough starter, and it’s a mixture of fresh flour, water, and some ripe starter. This mixture will be used entirely in a batch of dough and has the same fate as the bread dough you’re mixing: you will bake it in the oven. But before that, it’s your preferment for the day’s dough, meaning it will leaven your dough (make it rise) and be responsible for the flavor produced through the byproducts of fermentation.
A levain is an off-shoot of your sourdough starter with a limited life.
You might also see the term “levain bread” or “pain au levain,” which are other names for sourdough bread. Because the term levain is French for leaven, which is almost always taken to mean naturally fermented bread, the term levain is often used synonymously with sourdough.
What is the point of making a levain?
Now that we know what a levain is (and isn’t), what purpose does it serve and why not just use your sourdough starter? To me, there are two main uses for a levain:
- You can use a levain to scale up the pre-ferment to satisfy a recipe that requires more pre-ferment than your starter can cover
- It’s a chance for you to alter the flavor and performance characteristics of the pre-ferment for a single bake
And remember, you can always use your sourdough starter instead of your levain, especially in a pinch (more on this later).
Let’s look at the above benefits of making a levain in more detail.
1. A levain lets you scale up your preferment
I maintain a relatively large sourdough starter I refresh twice daily. At each refreshment time, once in the morning and once in the evening, I have about 150-200g of ripe starter ready. This starter can go into a dough mix, or I can use it to make a new levain. And while this amount of starter can cover just about all the recipes here at my site, a levain lets you scale up your preferment. And this can be essential if you maintain a smaller sourdough starter or your recipe requires a large preferment.
Further, using a levain means I can maintain a smaller sourdough starter to reduce flour use, and then in one step, I can build up my preferment to cover larger recipes or make multiple recipes.
2. A levain lets you change the flavor profile
You can use a levain to skew the flavor profile of the bread toward a more sour sourdough bread, or one that’s less sour. And the power of using a levain means you don’t have to modify your starter: you change the makeup of the levain.
Adjusting the flavor profile is an in-depth topic. But in general, and assuming other factors (temperature, seed percentage, etc.), I find a levain made with a higher percentage of whole grain flour brings more sourness to the final bread. Therefore, for many of the sweet or delicately flavored recipes here (like my sourdough babka), I make a levain with 100% white flour.
As an example, let’s look at that babka levain in detail to assess why it results in a milder result. Using white flour reduces the buffering capacity of the mixture. This reduced buffering capacity means the pH will drop faster as the byproducts of fermentation—namely, acids—are produced, acidifying the levain. Bacterial (lactobacilli) activity is reduced at low pH, which helps limit acid (sourness) production in the eventual dough.
Remember that the flour makeup of the levain is not the only factor affecting the eventual flavor profile. You must also account for fermentation time, temperature, starter seed percentage, and when you use it. All of these contribute to adjusting the end flavor balance. But this is just one of the levers we can pull to change the flavor and texture.
As sourdough bakers, part of the fun in natural leavening is managing wild yeast and bacteria to produce bread with our desired flavor profile.
Can a levain be multiple builds?
Yes. Many bakers use multiple levain builds to further adjust the balance of yeast to bacteria or for scheduling purposes. Some rye bread methods, such as 3-stage Detmolder rye, use multiple builds to favor either lactic acid bacteria or yeast (or each in succession). Another example is panettone, which uses a series of short “refreshment” builds with a bit of the lievito madre or pasta madre (sourdough starter), before it’s mixed into the primo impasto or first dough.

What if I forgot to make my levain?
In a pinch, just use your ripe sourdough starter! It might not have the same intended flavor profile in the end, but it’s better than not baking, right?
Alternatively, you could make an intermediate, fast levain build. In this case, I’ll often make a 100% flour, 100% water, 100% ripe starter (1:1:1 ratio). This levain is equal parts flour, water, and ripe sourdough starter and will ripen in 3-4 hours at 78-80°F/25-26°C. Again, this might adjust the final, intended flavor profile, but it’s a handy option.
How much levain is in sourdough bread?
The percentage of levain to total flour can change from recipe to recipe. A typical levain percentage for my formulas range from 6% to 30% levain in my final dough. But you can undoubtedly have values outside this range. The amount I use depends on the overall formula and its ingredients.
Note that the levain percentage in a bread formula differs from the prefermented flour percentage. See my post on baker’s percentages for more.
Is there a single levain recipe?
There’s no single levain recipe for every sourdough bread. And for the reasons just discussed above, I often change my levain builds to adjust the flavor profile, the flour mix, the dough’s hydration, and the timetable. There are many ways to make a levain, depending on the bread you’re baking.
What is a Levain and How is it Different From a Sourdough Starter?
To sum up, here’s what’s different, and the same, between a levain and a sourdough starter:
| Sourdough Starter | Levain |
|---|---|
| A preferment | A preferment |
| On-going culture, refreshed regularly | Used once for a single bake |
| Usually refreshed with same flour | Can be any flour combination |
| Because it’s maintained consistently, it should have consistent flavor characteristics | Can be used to change the flavor and texture of a single batch of dough |
Ultimately, what you call your sourdough starter, mother dough, chef, levain, etc., is up to you. Much of this is cultural, and each culture seems to have its terminology, but it’s also a preference. They’re all preferments, and they all help bring flavor, aroma, and keeping qualities to your bread. I use levain to represent a single off-shoot of my sourdough starter. And I use the term starter to represent my continually maintained sourdough culture.
What do you call yours?
What’s Next?
Now that you’ve created your levain, see the next step in the bread-making process, the autolyse technique (just before mixing).
Or, head back and see all 8 steps to making sourdough bread in the Beginner’s Guide to Sourdough Bread.





